Writes Dr. Theodosius BisdaAssoc. Professor of Vascular Surgery, Athens Medical Center

What is ventilation?
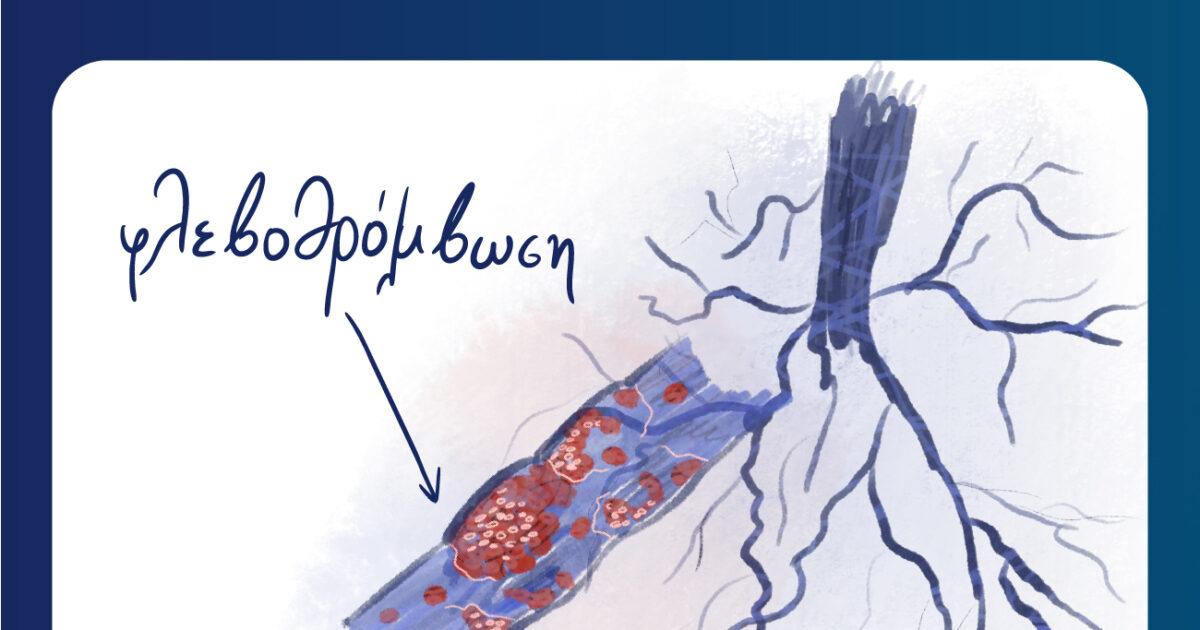
OR venous It is the creation of a blood clot in a vein, usually in the lower extremities. THE clot It can prevent normal blood flow, causing potentially serious complications. It is a “insidious” disease, as symptoms can confuse both the patient and the doctor, which makes it dangerous.
Causes of ventilation
OR venous can be caused by various factors such as:
• Παρατεταμένη ακινησία (π.χ. μετά από χειρουργείο ή μακρινό ταξίδι)
• Παχυσαρκία
• Κάπνισμα
• Χρήση αντισυλληπτικών χαπιών ή ορμονικών θεραπειών
• Οικογενειακό ιστορικό θρόμβωσης
• Καρκίνος και θεραπείες όπως η χημειοθεραπεία
• Τραυματισμοί ή χειρουργικές επεμβάσεις που επηρεάζουν τις φλέβεςWhat symptoms causes venous
Although ventilation can be asymptomatic, when manifested, the most common symptoms of venous thrombosis include:
• edema (swelling) in the affected end
• Pain or sensitivity, especially in the calf
• Redness and heat at the point of thrombosis
• Weight feeling on foot
What is pulmonary embolism and how is it associated with ventilation?
OR pulmonary embolism It is a potentially life -threatening condition that occurs when a clot from a peripheral vein, usually from the lower extremities, is detached and transported through the bloodstream to the lungs. There it can block a pulmonary artery, preventing proper oxygenation of the blood.
With what symptoms does the pulmonary embolism manifest?
OR pulmonary embolism manifests with vigorously and suddenly symptoms such as:
• Δύσπνοια
• Πόνος στο στήθος που επιδεινώνεται με την αναπνοή
• Ταχυκαρδία
• Βήχας, μερικές φορές με αιμόπτυση
• Αίσθημα λιποθυμίας ή ζάλη
• ΣυγκοπήBecause pulmonary embolism is an urgent medical condition, early diagnosis and treatment is critical for the patient’s survival.
How is the diagnosis of venous thrombosis achieve?
The diagnosis of venous thrombosis is based on a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests. The most common methods include:
• Υπερηχογράφημα με Doppler (τρίπλεξ), το οποίο μπορεί να ανιχνεύσει την παρουσία θρόμβου στις φλέβες.
• Αιματολογικές εξετάσεις (D-dimer test), οι οποίες μετρούν την παρουσία προϊόντων διάσπασης θρόμβων στο αίμα.
• Αξονική αγγειογραφία, ειδικά όταν υπάρχει υποψία πνευμονικής εμβολής.Why does venous thrombosis need immediate treatment?
The early diagnosis and treatment of venous thrombosis It is vital, as it can prevent serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism. The treatment of venous thrombosis includes:
• Αντιπηκτικά φάρμακα, τα οποία μειώνουν τον κίνδυνο επέκτασης του θρόμβου και νέων θρομβώσεων.
• Θρομβολυτικά φάρμακα, που χρησιμοποιούνται σε βαριές περιπτώσεις για να διαλύσουν τον θρόμβο.
• Χειρουργικές ή ενδοαγγειακές παρεμβάσεις, σε περιπτώσεις όπου η φαρμακευτική αγωγή δεν επαρκεί.In addition, prevention is just as important. Regular movement, use of special compression socks and avoiding risk factors, such as Smoking and sedentary life.
OR venous and the pulmonary embolism are two interrelated diseases with serious consequences. Timely recognition and treatment is crucial to prevent complications and maintaining the patient’s health.
Contact directly with his clinic Dr. Theodosius Bisda for specialized diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic approach.